Meat Cuts Explained: Your Ultimate Guide To Different Cuts of Beef
What is Meat?
Meat is the muscle of animals used as food, which only becomes edible after two fundamental events: bleeding and maturation.
The various meats, whatever the animal species they come from, have an equal nutritional value, as they provide a high percentage of protein, composed of essential amino acids (which the body cannot produce), an appreciable amount of iron, B-complex vitamins and vitamin PP.
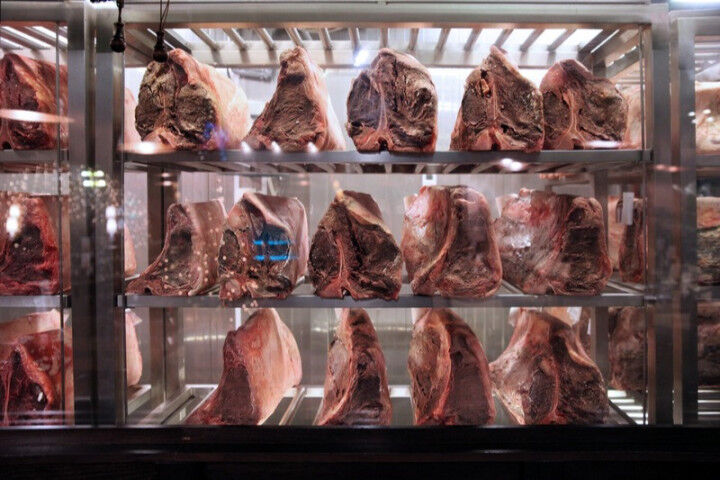
What is Meat Maturation or Hanging?
It is the maturation or aging of meat, its unprocessed preservation above freezing point.
What is the purpose of Meat Maturation?
Its main purpose is to tenderize the meat, but this can only be achieved within certain limits, as other factors also contribute to tenderness. The more connective tissue is present, the less tender the meat is, and the greater the muscle contraction, the lower the tenderness.
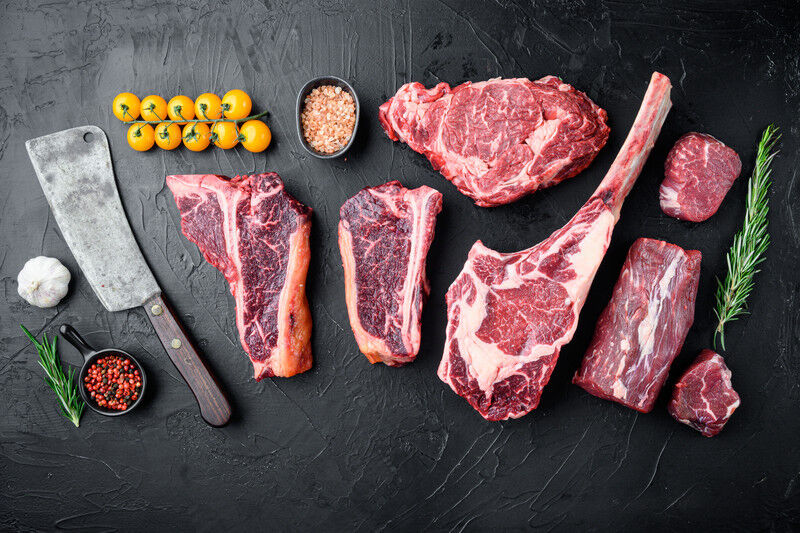
What are the Different Cuts of Meat?
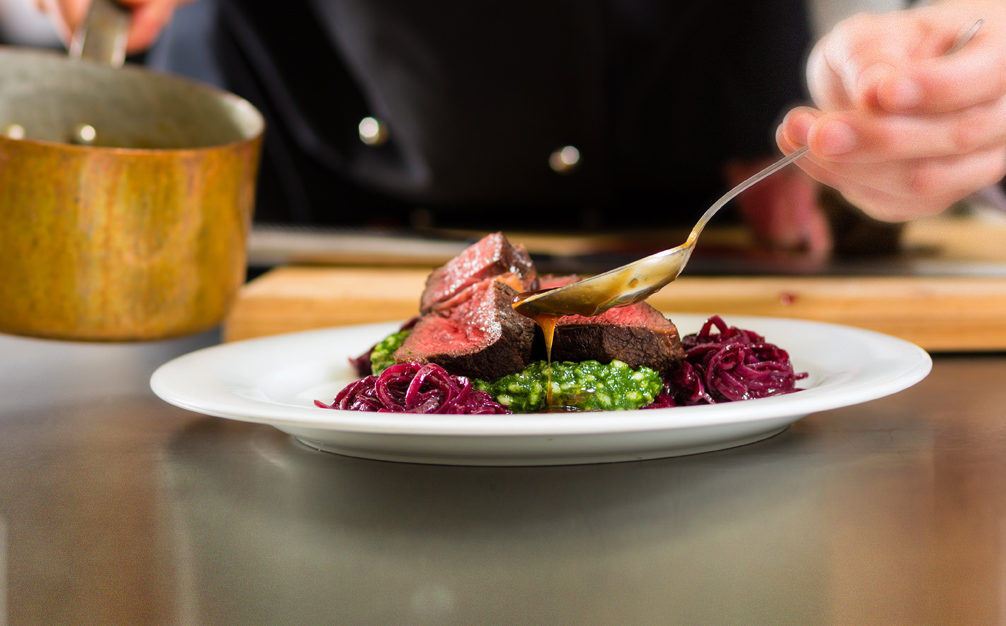
Different cuts of meat
There are two determining factors:
- Only with animals fed balanced diets based on quality cereals and legumes, without by-products and high-protein cores is it possible to process and cook meat with skill and satisfaction.
- The cutting of meat must always follow the direction of the muscle fibres
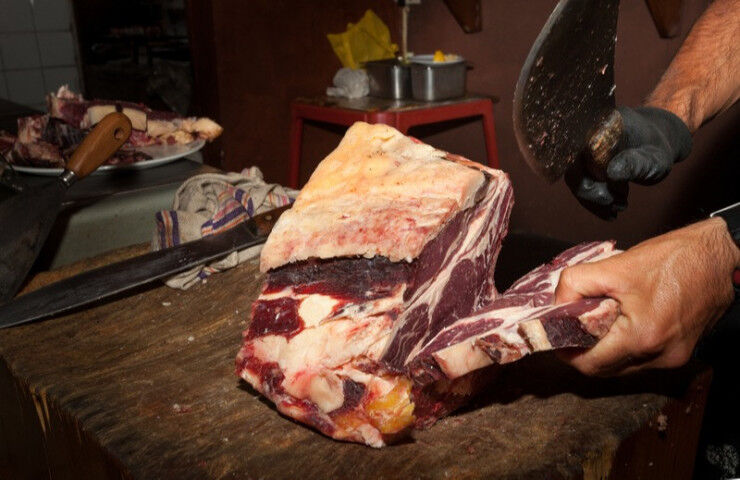
The (adult) bovine tends to be divided into half-carcases by cutting along the spinal column. A half-carcase is defined as the eviscerated animal, cut exactly in half, without head or tail.
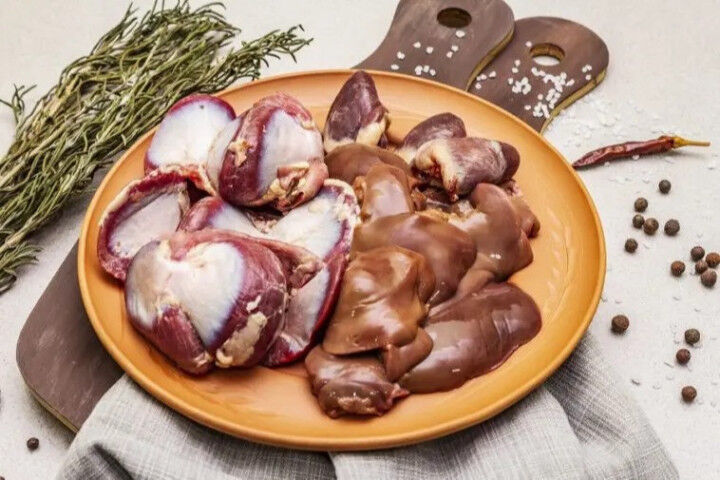
The Fifth quarter
This consists of the thoracic and abdominal organs, as well as the extremities (legs, tail, head) and blood. Particularly in the past, it was the basis of Italian cuisine since only the rich could eat the ‘valuable’ parts, while the people only used the offal.
Unlike meat, offal must be eaten fresh in the first 24 or 36 hours, without being matured.
Of the fifth quarter, a distinction must be made between offal, which are the internal organs, and sweetbreads, which are the salivary glands and pancreas.
- Blood, head, brains, cheek, tongue.
- Lungs, heart, liver, pancreas, spleen.
- Kidneys, stomachs, intestines, spinal cord.
- Breast, feet, testicles, tail, eye, diaphragm.